Scaling RAG Systems in Financial Organizations Artificial intelligence has emerged...
Read MoreEnsuring AI ACT Compliance: Best Practices for Today's Businesses
Table of Contents
ToggleThe European Union is tackling artificial intelligence head-on with the AI Act, an ambitious draft regulation aimed at establishing the first comprehensive #legal framework for this technology. The act aims to ensure the #responsible development and use of AI. According to the latest PwC study: 60% of companies are not yet ready to comply with the AI Act.

In this article, we’ll look at the different elements of AI Act laws and best practices for businesses to follow.
What does AI Act mean?
The Artificial Intelligence Act, or AI Act, is an important piece of legislation that was created to control the application and implementation of AI technology in the European Union (EU). It acts as a framework to make sure AI systems created and used in the EU follow specific safety, accountability, and transparency requirements.
In order to ensure that AI technologies are applied morally and sensibly and reduce hazards to both people and society at large, they must adhere to a set of strict guidelines. The AI Act covers a number of topics, including defining high-risk AI applications, creating conformity assessment protocols, and specifying consequences for noncompliance. Its overall goal is to establish a compromise between protecting fundamental rights and encouraging innovation.
In addition, the AI Act is a proactive approach by legislators to deal with the increasing complexity of AI-related technology. It seeks to promote consumer and business trust and confidence in AI systems by establishing explicit rules and responsibilities.
The AI Act also reflects the EU’s commitment to establishing international norms for AI governance, opening the door for a unified strategy for cross-border regulation. The legislation aims to establish a strong framework that encourages the responsible and ethical use of AI by engaging in dialogue and cooperation with a range of stakeholders, including academics, industry experts, and civil society. This will ultimately aid in the development of an EU digital single market.
AI Act Adoption: A Multi-Step Journey Until 2026
Formal Adoption:
Parliamentary Vote: The European Parliament will convene a plenary vote to formally adopt the AI Act’s final language after reaching a preliminary agreement in December 2023. This may happen by 2024’s end.
Approval by the Council: The final text must also get formal endorsement from the Council of the European Union, which represents the member states. Usually, this action comes after the vote in the Parliament.
Publication and Entry into Force (Estimated: Early 2025):
Publication in the Official Journal: The AI Act will be published in the European Union’s Official Journal upon approval by the Council and the Parliament. This signifies the formal enactment of the law.
Grace Period: There will probably be a few months’ grace period after publishing. This gives businesses and participating states time to adapt to the new rules and get ready for their implementation.
Compliance Period (2025-2026):
Regulation Awareness: During this time, firms and pertinent stakeholders will be made aware of the requirements of the AI Act through the launch of awareness campaigns and instructional materials.
Measures for Compliance: Businesses in the EU that create, implement, or use AI systems will have about a year to change their operations so that they conform to the Act’s requirements. This includes documentation, risk analyses, and maybe even changing the AI systems themselves.
National Implementation: It will be the duty of the EU member states to incorporate the AI Act into their respective national legislation. This might entail appointing national oversight organizations and developing certain enforcement procedures.
Enforcement (2026+):
Audits and Inspections: The AI Act will be enforced following the conclusion of the compliance period. To guarantee conformity, member nations may undertake audits and inspections of businesses.
Sanctions: Organisations that violate the AI Act may be subject to penalties or possibly prohibitions on the use of particular AI systems.
Constant Monitoring: To guarantee continued adherence to the AI Act, regulatory agencies will probably set up continual monitoring procedures.
Exploring Regulatory Frameworks and Standards of AI act
Regulatory Framework of the AI Act:
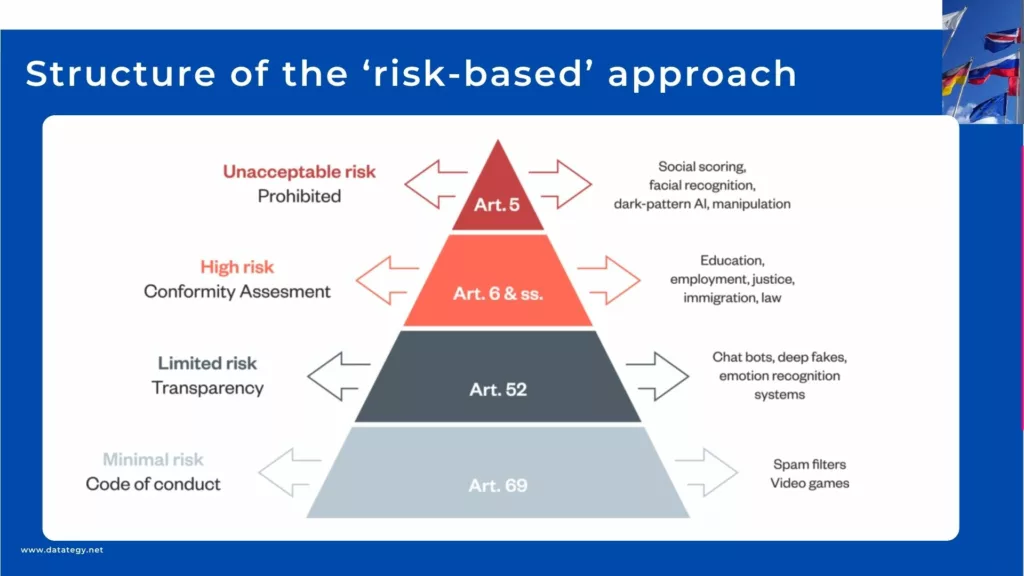
Risk-Based Approach
AI systems are categorized by the AI Act according to their possible effects. Unacceptable risk systems are outright prohibited, such as social scoring with tangible repercussions. Regulations governing high-risk systems, such as facial recognition, are strict. Strong human control, precise risk assessments, and thorough documentation of training data and algorithms are a few of these. Chatbots and other medium-risk systems need to be transparent about their decision-making process and implement risk management techniques.
Although there are less restrictions for low-risk systems, they nevertheless need to abide by data protection rules and refrain from deceiving consumers. By ensuring that rules are appropriate for various uses, this risk-based approach promotes innovation while reducing possible harm.
Transparency and Explainability
Transparency in AI decision-making is emphasized under the AI Act, especially for high-risk systems. It’s required of developers to explain how their AI generates its results. This might include describing the methods that were employed, the data that were used, and the logic that went into the choice that was made.
The AI Act seeks to boost public confidence by providing accessible explanations and permitting human involvement when needed. Furthermore, managing expectations and preventing misuse can be aided by providing explicit information about the constraints and potential biases of AI systems.
Data Governance
The AI Act places a strong emphasis on the necessity of collecting, storing, and using data responsibly. This complies with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) guidelines set out by the EU.
It will be the responsibility of developers to guarantee that the data used for training AI models is impartial, representative, and authorized. There will be safeguards in place to stop discriminatory behaviors that could result from skewed data. Additionally, the Act promotes data reduction or utilising just the information required for a particular AI function.
Human Oversight
From development and deployment to operation and monitoring, the AI Act encourages human supervision at every stage of the AI lifecycle. By doing this, possible dangers are reduced and crucial choices are kept under human control.
A dedicated human reviewer may be needed for high-risk systems in order to approve particular decisions or step in during urgent situations. The Act also highlights the significance of human-centered design, which guarantees that AI systems are created to enhance rather than subsume human capacities.
Best Practices to be AI Act Compliant
1- Strong Governance Structures
Businesses who want to comply with the AI Act need to set up strong governance frameworks. This entails establishing distinct chains of command, accountability, and supervision for every AI-related activity carried out by the company.
These kinds of arrangements guarantee that decision-making procedures are open and compliant with moral and legal requirements. Mechanisms for risk assessment, ethical review, and continuous AI system monitoring are all part of strong governance frameworks. Companies can efficiently manage the creation, application, and use of AI technology while reducing risks and guaranteeing regulatory compliance by putting these frameworks in place.
Demystifying AI: A Comprehensive Guide to Key Concepts and Terminology
This guide will cover the essential terminology that every beginner needs to know. Whether you are a student, a business owner, or simply someone who is interested in AI, this guide will provide you with a solid foundation in AI terminology to help you better understand this exciting field.

2- Measures for Data Security and Privacy
Maintaining the security and privacy of data is essential for AI Act compliance. For the safeguarding of confidential and critical information during the AI process, companies must establish robust data security protocols. This involves adhering to data protection standards, which include limiting data usage, reducing its volume, and ensuring the safety of data processing activities.
Companies may ensure regulatory compliance and uphold confidence with customers and stakeholders by placing a high priority on data privacy and security. This helps to reduce the risks associated with data breaches, unauthorized access, and misuse of personal information.
3- Transparency and Explainability of the Models
Explainability and transparency are essential components of AI Act compliance. Making AI systems visible to consumers, regulators, and other parties should be a top priority for businesses. This means making data sources and processing techniques public, facilitating people’s comprehension and contestation of automated conclusions, and offering concise explanations of how AI algorithms arrive at decisions.
Companies may establish trust with stakeholders, allay worries about bias and prejudice in AI, and show their dedication to the development and use of ethical AI by promoting openness and explainability.
4- Redress Mechanisms for AI Bias and Discrimination
Organizations should set up procedures for dealing with and resolving cases of prejudice and discrimination in AI systems. This involves putting in place procedures for keeping an eye out for and identifying biases in AI algorithms, as well as channels for hearing complaints from those impacted by unfair or biassed rulings and handling them.
Businesses should create policies for looking into and fixing cases of prejudice and discrimination in AI systems, as well as processes for apologising, explaining, and helping those who have been harmed. Companies may maintain regulatory compliance, reduce the risk of injury and prejudice, and preserve the ideals of justice, accountability, and transparency in their AI operations by putting in place redress procedures.
5- Awareness and Training of Employees
For AI Act compliance, funding staff awareness and training initiatives is essential. Employees engaged in AI development, deployment, and usage should get thorough training from companies to guarantee they are aware of their duties and responsibilities under the AI Act.
Topics include data privacy regulations, security measures, ethical AI principles, and AI system-specific compliance needs should all be included in training programmes. Businesses may promote a culture of compliance, reduce human error, and improve overall organisational preparedness to fulfil regulatory requirements by providing staff with the information and abilities needed to handle ethical dilemmas and complicated regulatory environments.
6- Maintaining Records and Documentation
To show that they are in conformity with the AI Act, businesses should place a high priority on meticulous documentation and record-keeping procedures.This includes keeping thorough documentation of all AI system development processes, training data sources, algorithmic choices, and model upgrades and adjustments.
By capturing these details, businesses may improve auditability, accountability, and transparency while monitoring the development of their AI systems and successfully handling regulatory requests and audits. Businesses may show their dedication to compliance and lessen the chance of fines for non-compliance by keeping thorough and accurate records.
How can papAI Platform help you to Address the AI Act Challenges?
Overview of papAI
papAI is an all-in-one AI solution and is distinct in that it serves as the engine for the efficient industrialization and execution of data science and AI projects. With one platform that blurs the lines between development, deployment, and collaboration, papAI aims to streamline the whole AI project lifecycle.
Modern technology, teamwork capabilities, and a set of tools for efficient project management are all included in this solution, which has been meticulously developed to give businesses a comprehensive approach to artificial intelligence.
papAI Platform provides a complete solution to assist companies in addressing the issues raised by the AI Act:
Risk Assessment and Management: papAI provides tools to conduct risk assessments for AI systems, allowing companies to categorize them based on the AI Act’s framework (unacceptable, high, medium, low-risk). This helps prioritize resources and align compliance efforts.
Data Governance and Lineage: The solution offers robust data governance capabilities. It helps track data lineage, ensuring companies understand the origin and flow of data used in AI models. This transparency is crucial for demonstrating responsible data collection and usage practices.
Data Quality and Bias Detection: papAI incorporates data quality checks to identify and address potential biases within datasets used for training AI models. This mitigates risks associated with discriminatory AI outcomes and helps comply with the AI Act’s emphasis on fair and unbiased systems.
Explainable AI (XAI): Our platform integrates explainability tools that provide insights into how AI models arrive at decisions. Companies can use these insights to explain model outputs, improve transparency, and address concerns raised by the AI Act regarding explainability, particularly for high-risk systems.
Model Versioning and Control: papAI facilitates model version control, allowing companies to track changes made to AI models over time. This detailed audit trail helps demonstrate responsible development practices and adherence to the AI Act’s requirements.
Security and Privacy by Design: Throughout the AI lifecycle, papAI platform fosters security and privacy. Data encryption and role-based access control are two features that guarantee sensitive data is safeguarded and complies with the data security and privacy guidelines of the AI Act.
In addition, papAI Platform has sophisticated security safeguards in place to protect confidential data and lessen the possibility of fines for noncompliance. Businesses may reduce regulatory risks, expedite compliance processes, and show a commitment to ethical and responsible AI usage by utilizing our platform.
To discover more about how papAI’s capabilities can help your organization address the requirements of the AI Act, explore our documentation for in-depth insights and demonstrations.

The Artificial Intelligence Act, or AI Act, is an important piece of legislation that was created to control the application and implementation of AI technology in the European Union (EU). It acts as a framework to make sure AI systems created and used in the EU follow specific safety, accountability, and transparency requirements.
Formal Adoption in 2024.
Publication and Entry into Force (Estimated: Early 2025).
Compliance Period (2025-2026).
Enforcement (2026+).
Risk-Based Approach
Transparency and Explainability
Data Governance
Human Oversight
1- Strong Governance Structures
2- Measures for Data Security and Privacy
3- Transparency and Explainability of the Models
4- Redress Mechanisms for AI Bias and Discrimination
5- Awareness and Training of Employees
6- Maintaining Records and Documentation
Interested in discovering papAI?
Our AI expert team is at your disposal for any questions
How AgenticAI is Transforming Sales and Marketing Strategies
How AgenticAI is Transforming Sales and Marketing Strategies Agentic AI...
Read More“DATATEGY EARLY CAREERS PROGRAM” With Abdelmoumen ATMANI
“DATATEGY EARLY CAREERS PROGRAM” With Abdelmoumen ATMANI Hello, my name...
Read MoreIntroducing the Error Analysis Tree: A Smarter Way to Improve AI Models
Introducing the Error Analysis Tree: A Smarter Way to Improve...
Read More


